**“Understanding Orbital Motors: Function, Applications, And Advantages”**
Certainly! Here’s an engaging introduction for your article titled **“Understanding Orbital Motors: Function, Applications, and Advantages”**:
---
In the world of hydraulic machinery and industrial automation, orbital motors stand out as powerful yet compact components that drive efficiency and precision. But what exactly makes these motors so essential across various industries? Whether you're an engineer, technician, or simply curious about advanced mechanical systems, understanding how orbital motors function, where they are applied, and the unique advantages they offer can open the door to smarter equipment choices and innovative solutions. Join us as we dive into the fascinating mechanics of orbital motors and explore why they continue to be a preferred choice in modern engineering.
---
Would you like me to tailor it to a specific audience or tone?
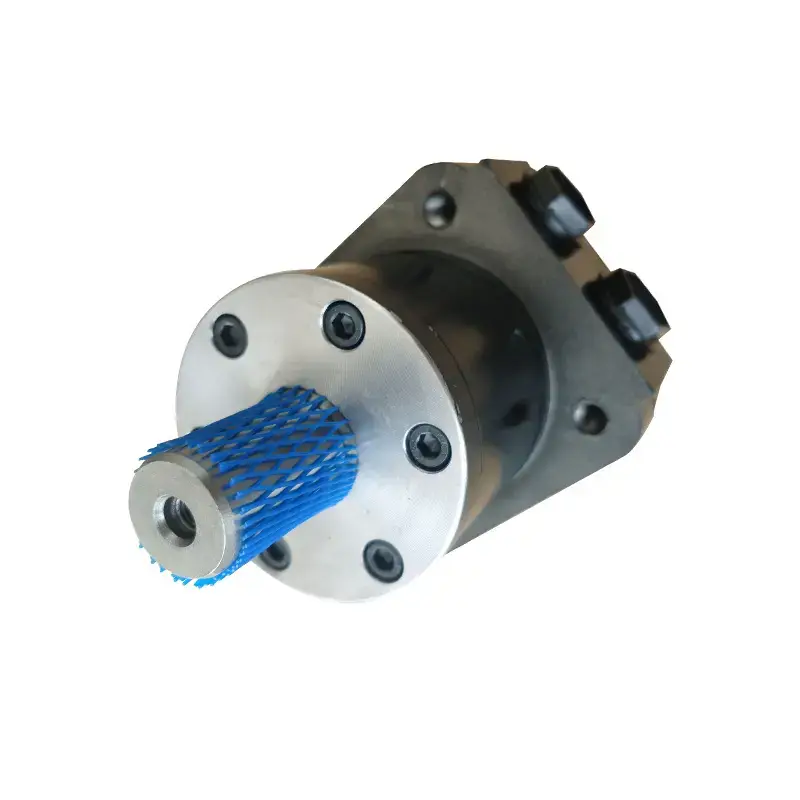

- Overview of Orbital Motors and Their Core Functionality
### Overview of Orbital Motors and Their Core Functionality
Orbital motors occupy a significant niche within the broader category of hydraulic motors, primarily distinguished by their unique design and operational principles. Often referred to interchangeably as gerotor motors or orbit motors, orbital motors combine simple construction with high efficiency, making them indispensable components in various industrial and mobile hydraulic applications. To fully appreciate the role and advantages of orbital motors, it is important to first understand their basic structure, working mechanics, and core functionality.
At its heart, the orbital motor is a type of positive displacement hydraulic motor, which means it converts hydraulic energy directly into mechanical energy utilizing a fixed volume of fluid per rotation. The term “orbital” describes the characteristic motion of the internal components of the motor as they revolve and generate torque. Unlike traditional gear motors, orbital motors function through the interaction of an inner rotor and an outer ring or stator, which results in smooth, continuous rotary motion.
The internal mechanism of an orbital motor comprises three main parts: a drive shaft, a multi-lobed inner rotor (commonly called the gerotor), and an outer ring with equally spaced internal gears or lobes. The lobes on the inner rotor mesh precisely with those on the outer ring. When pressurized hydraulic fluid enters the motor, it flows into chambers formed between the rotor lobes and the motor housing. The fluid pressure forces the rotor to "orbit" inside the outer ring without actually rotating on its axis, which in turn causes the drive shaft to rotate and deliver mechanical output.
This orbital motion results in a relatively uniform torque output throughout each revolution, minimizing vibrations and mechanical noise compared to other motor types such as vane or gear motors. Due to this smooth and quiet operation, orbital motors are preferred in applications that demand lower noise levels, precise control, and consistent torque performance.
Another key aspect of orbital motors is their ability to operate effectively at various speeds and pressures. The flow rate of the hydraulic fluid correlates to the motor’s speed, whereas the pressure differential determines the torque generated. This predictable relationship makes orbital motors highly controllable and easy to integrate into complex hydraulic systems. Moreover, the design inherently provides a self-lubricating mechanism, as the hydraulic fluid used for power transmission simultaneously lubricates internal components, reducing wear and extending service life.
Orbit motors are also known for their compact design and lightweight construction relative to the torque output they can generate. This efficiency in size and weight allows for their deployment in applications where space constraints and weight limitations are critical considerations. They are commonly found in machinery such as agricultural equipment, construction vehicles, industrial conveyors, forestry machinery, and marine vessels.
One of the defining features of the orbital motor's core functionality is its fail-safe design in the event of pressure loss or fluid contamination. Unlike some hydraulic motors that may seize or suffer catastrophic failure under adverse conditions, the simple and robust nature of the orbital motor means it can absorb transient conditions without significant damage. This ruggedness, combined with ease of maintenance, enhances machine uptime and reliability — vital parameters in demanding industrial environments.
Summarizing the operation from a technical perspective, orbital motors convert the energy stored in pressurized hydraulic fluid into rotational power via the orbiting action of the inner rotor against the external ring. The geometry of the gerotor creates sealed chambers that expand and contract as the rotor moves, facilitating fluid intake, pressurization, and exhaust within a single rotation cycle. This cyclical chamber volume variation is the crux of the fundamental function of the orbital motor.
In addition to the basic operation, advancements in material science and manufacturing technologies have improved the performance and durability of orbital motors. Modern orbital motors often feature enhanced seals, precision-machined components, and corrosion-resistant materials that extend operational life and increase efficiency across broader operating ranges. This continues to solidify their status as a preferred choice for countless hydraulic power transmission challenges.
In conclusion, orbital motors embody a blend of simplicity and efficiency in hydraulic drive technology. Their core functionality—transforming hydraulic energy into smooth, reliable rotational motion through the orbiting action of intermeshing rotors—offers unique advantages in control, noise reduction, size, and durability. The versatility and robustness of orbital motors have made them a cornerstone of mobile and industrial hydraulic systems worldwide.
- Key Components and Working Principles of Orbital Motors
**Key Components and Working Principles of Orbital Motors**
Orbital motors are a specialized category of hydraulic motors widely used in various industrial and mobile applications due to their compact design, high torque output, and smooth operation. Understanding the key components and working principles of orbital motors is essential for appreciating their functionality and why they have become a preferred choice in hydraulic power systems. This section delves deeply into the fundamental elements that make up an orbital motor and explains how these components work synergistically to convert hydraulic energy into mechanical motion efficiently.
At the core of every orbital motor lies the **gerotor mechanism**, which is the primary component responsible for generating torque and rotational motion. The gerotor assembly typically consists of an internal rotor and an external ring gear with one more tooth than the rotor. The internal rotor has fewer teeth and is eccentrically mounted inside the external ring. When high-pressure hydraulic fluid enters the motor, it acts on the crescent-shaped chambers formed between these two components, causing the internal rotor to rotate. This eccentric rotation of the internal rotor inside the ring gear produces a smooth, continuous output shaft rotation—a defining characteristic of orbital motors.
Complementing the gerotor is the **cam ring** or sometimes referred to as the stator housing, which plays an essential role in maintaining the tight tolerances and sealing needed for efficient operation. The cam ring encloses the internal components and provides structural support while ensuring minimal leakage between adjacent chambers. This sealing ability is critical for sustaining pressure differentials that directly impact the motor's torque and speed capabilities. The cam ring also acts as a guide that keeps the internal rotor correctly aligned during operation, preventing mechanical failures and reducing wear over time.
The **input and output ports** are other crucial parts of the orbital motor. Hydraulic fluid enters through the input port under controlled pressure and flows through the fixed-volume chambers created by the gerotor and cam ring. As the fluid expands these chambers, it generates torque applied to the motor’s output shaft. The output shaft transmits this mechanical rotation to perform work, usually connected to a gearbox, conveyor, winch, or any machinery requiring rotary motion. The output shaft is typically supported by robust bearings to handle radial and axial loads, ensuring smooth rotation and longevity of the motor.
Another critical feature in orbital motors is the **valve plate or distribution plate**, which directs the flow of hydraulic fluid into different chambers at the appropriate time, coordinating the timing of the fluid flow to generate continuous motion. This plate ensures efficient fluid management inside the motor, prevents pressure spikes, and minimizes energy losses, contributing to the overall high volumetric efficiency of orbital motors.
From a working principle perspective, orbital motors operate based on the balanced interaction between hydraulic pressure and mechanical motion. The key to their function is the conversion of pressurized hydraulic fluid energy into rotational torque through the incremental movement of the gerotor set. When pressurized fluid flows into the motor, it pushes against the chambers formed between the internal rotor teeth and the external ring gear. This pressure causes the internal rotor to orbit within the housing, creating continuous rotation without the pulsations typically found in other hydraulic motor types. The orbiting movement reduces internal friction and wear while improving smoothness and reliability.
A unique aspect of orbital motors is their ability to generate high torque at low speeds without requiring large volumes of fluid flow. This trait makes orbital motors especially suitable for applications such as industrial screwdrivers, winches, wheel drives for mobile machinery, and augers. Their robust design, combined with the compact gerotor mechanism, allows them to operate efficiently in both low-speed, high-torque, and moderate-speed ranges.
Furthermore, the internal construction of orbital motors inherently provides excellent self-lubrication and cooling capabilities. Since the hydraulic fluid is continually circulated through the motor, it lubricates internal components and dissipates heat generated from friction, which enhances durability and operational life. The balanced loading on gears and seals due to the orbiting action also reduces mechanical stress, minimizing maintenance needs.
In conclusion, the key components of an orbital motor—the gerotor assembly, cam ring, valve plate, input/output ports, and output shaft—work together harmoniously to convert hydraulic pressure into smooth, efficient rotational torque. The working principle hinges on the orbiting motion of the internal rotor within the external ring, driven by precisely controlled hydraulic fluid flow, resulting in an efficient, compact, and versatile hydraulic motor that meets a wide array of industrial demands. Understanding these components and how they interact in the orbital motor provides insight into why this type of motor remains a staple in hydraulic power transmission across many industries.
- Common Industrial and Commercial Applications of Orbital Motors
**Common Industrial and Commercial Applications of Orbital Motors**
Orbital motors, also known as gerotor motors, are widely recognized for their compact design, high torque output, and efficient performance in various industrial and commercial settings. These motors convert hydraulic energy into mechanical rotation through a unique orbital motion, which allows them to deliver smooth, reliable power in applications demanding durability and precision. Understanding the common industrial and commercial applications of orbital motors highlights their versatility and explains why they are favored across numerous sectors.
One of the most prevalent uses of orbital motors is in **material handling equipment**. Forklifts, pallet jacks, and scissor lifts commonly rely on orbital motors to power their hydraulic systems. The compact size of orbital motors enables integration into small spaces within the machinery, while their high torque capacity provides the force necessary to lift and maneuver heavy loads efficiently and safely. Their smooth operation reduces shock loads and wear on other mechanical components, enhancing equipment longevity.
In the **agricultural sector**, orbital motors play a crucial role in driving equipment that requires reliable and continuous operation under harsh conditions. Machines such as combine harvesters, sprayers, and conveyors utilize orbital motors for their drive systems. The motors’ ability to function efficiently with varying hydraulic flow rates makes them well suited to agricultural implements where operating speeds fluctuate frequently. Furthermore, their robust design ensures minimal downtime, critical during peak farming seasons.
The **construction industry** benefits significantly from orbital motors, especially in machinery like excavators, concrete mixers, and drilling rigs. Construction machines often operate in demanding environments requiring motors that can handle heavy loads and resist contamination such as dirt and dust. Orbital motors are favored because of their sealed design and internal lubrication, which contribute to excellent durability and reliability on construction sites. Their high starting torque allows construction equipment to perform tasks such as breaking ground or lifting heavy materials without stalling.
In the **marine sector**, orbital motors are used in winches, steering systems, and deck machinery aboard vessels. These applications demand motors that can produce consistent power and withstand corrosive environments compounded by saltwater exposure. Orbital motors with corrosion-resistant components and protective coatings offer reliable performance despite the harsh marine conditions while maintaining smooth controllability, crucial for vessel maneuvering and cargo handling.
The **automotive industry** increasingly incorporates orbital motors in manufacturing automation and assembly lines. They power conveyor belts, robotic arms, and hydraulic lifts used in vehicle assembly processes. The precise speed control and high efficiency of orbital motors contribute to accelerated production rates and reduced energy consumption. Besides manufacturing, orbital motors are also used in off-road vehicles, such as utility terrain vehicles (UTVs) and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), where compact design and strong torque output improve vehicle maneuverability in challenging terrains.
Orbital motors find essential applications in **industrial automation and packaging** as well. Machines performing tasks like bottle filling, labeling, and materials packaging rely on these motors due to their ability to deliver precise and repeatable torque in low-speed, high-torque applications. Their quiet operation and smooth start-stop characteristics minimize vibrations and mechanical stresses, preserving delicate packaging materials and improving overall system accuracy.
Another key area is the **mining industry**, where orbital motors drive heavy-duty equipment such as drilling rigs, crushers, and conveyors. Mining operations require machinery capable of sustained high performance in abrasive and dusty conditions. Orbital motors offer the mechanical strength and hydraulic efficiency needed to cope with the continuous, demanding workloads common in mining environments, reducing maintenance intervals and increasing operational uptime.
Finally, in the **forestry sector**, orbital motors are often utilized in equipment like feller bunchers, skidders, and sawmills. The ability of orbital motors to provide reproducible torque at varying speeds is advantageous for operations where precision and power are vital in cutting and transporting heavy timber. Their robust construction ensures the motors withstand rough handling and extreme outdoor conditions.
Through these varied applications, the orbital motor proves itself as a versatile component capable of addressing the challenges posed by multiple industries. Its compact footprint, superior torque characteristics, and endurance under tough operating conditions make it an indispensable technology in both industrial and commercial domains.
- Benefits of Using Orbital Motors in Various Systems
**Benefits of Using Orbital Motors in Various Systems**
Orbital motors have become an indispensable component in a wide array of mechanical and hydraulic systems due to their unique design and operational characteristics. These motors are also known as gerotor or geroler motors, and their compact construction, smooth torque delivery, and exceptional efficiency offer significant advantages across multiple industries. Understanding the benefits of using orbital motors in various systems allows engineers and users to optimize performance, reduce costs, and achieve superior reliability. This section delves into the primary advantages orbital motors deliver when integrated into diverse applications.
One of the most prominent benefits of orbital motors is their **compact size and lightweight design**. Unlike traditional hydraulic motors, orbital motors achieve high torque output within a relatively small footprint. This feature is especially critical in applications where space constraints are a limiting factor, such as mobile machinery, agricultural equipment, and aerial platforms. The ability to deliver substantial power without demanding excessive installation room enables designers to create more compact and efficient systems, enhancing overall machine maneuverability and reducing weight.
Another key advantage is the **smooth and consistent torque output** characteristic of orbital motors. Their internal gerotor mechanism provides a steady flow of power without pulsations or sudden torque spikes. This smooth operation translates into reduced vibrations and mechanical stress on connected components, which significantly increases the lifespan of systems and decreases maintenance requirements. Systems such as conveyor belts, winches, and hydraulic drives benefit considerably from the gentle torque characteristics, ensuring operational stability and safety.
**High reliability and durability** are also notable benefits associated with orbital motors. Their simple yet robust internal construction minimizes the number of wear-prone parts, reducing the likelihood of mechanical failure. Additionally, orbital motors are highly resistant to contamination and can tolerate lower-quality hydraulic fluids better than many other motor types, which is invaluable in harsh environments like construction sites or mining operations. This resilience enhances system uptime, lowers downtime costs, and contributes to more predictable maintenance schedules.
Efficiency is another critical benefit. Orbital motors typically operate with **high volumetric and mechanical efficiency**, which means better energy conversion from hydraulic fluid to mechanical power. This results in reduced fuel or power consumption for machines powered by hydraulic systems, directly translating into cost savings and less environmental impact. In industries such as forestry, marine, and industrial automation, where operational time and fuel costs are major considerations, the efficiency gains provided by orbital motors are highly advantageous.
Orbital motors also exhibit **versatility in control and application**. They can operate effectively at varying speeds and loads, making them suitable for a broad spectrum of uses—from precise industrial actuators to heavy-duty vehicle propulsion. Their ability to work well with variable displacement pumps enhances system adaptability and responsiveness, critical in modern systems that demand dynamic performance. As a result, orbital motors are used in systems ranging from agricultural sprayers and skid steer loaders to marine winches and industrial mixers.
Moreover, orbital motors possess excellent **starting torque characteristics**, delivering high torque at low speeds without stalling. This makes them ideal for applications requiring strong initial movement or consistent torque under load, such as lifting equipment, hydraulic drives for turntables, or drilling rigs. The high starting torque ensures that the systems can handle demanding operational conditions without requiring oversized components or excessive power input.
Additionally, the **ease of installation and maintenance** of orbital motors is a practical benefit that improves operational efficiency. Their compactness and standardized mounting configurations simplify integration into existing systems, minimizing downtime during upgrades or repairs. Maintenance procedures tend to be straightforward due to the modular nature of their internal components, and many orbital motors are designed to be serviced without complete disassembly, further reducing operational interruptions.
In summary, orbital motors stand out for their combination of compact design, smooth torque, high reliability, efficiency, and versatility, providing substantial benefits across diverse mechanical and hydraulic systems. Their integration leads to improved system durability, enhanced performance, and reduced operational costs, making them a preferred choice in many demanding industrial, agricultural, and mobile machinery applications.
- Future Trends and Innovations in Orbital Motor Technology
**Future Trends and Innovations in Orbital Motor Technology**
Orbital motors, known for their robust design, smooth operation, and high torque-to-weight ratio, have long been integral components in various industrial applications. As technology advances and industries demand higher efficiency and precision, the evolution of orbital motor technology is shaping up to be a dynamic field enriched with innovative trends. These advancements not only aim to enhance performance and reliability but also contribute toward sustainability and smarter operation in diverse applications spanning construction machinery, agricultural equipment, material handling, and many others.
One of the most prominent future trends in orbital motor technology is the integration of **smart sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities**. Today’s orbital motors primarily focus on mechanical efficiency, but embedding sensors that monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, vibration, and rotational speed in real time can revolutionize the way these motors are utilized. Through IoT connectivity, orbital motors will be able to transmit performance data constantly to control systems or cloud platforms, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime by forecasting failures before they occur. This real-time monitoring contributes to operational efficiency, extends equipment lifespan, and significantly reduces maintenance costs.
In addition to smart monitoring, **advances in materials science** are driving innovation in orbital motors. Researchers are experimenting with lightweight yet stronger composite materials and advanced alloys, aiming to reduce the overall weight of the motor while boosting durability and thermal performance. Such improvements can enhance the motor’s power density and efficiency, making orbital motors more suitable for applications where weight and space constraints are critical, such as robotics and aerospace segments. Moreover, better heat dissipation materials help combat overheating issues frequently faced during continuous high-load operation, thus improving reliability.
The push for greater energy efficiency is another significant catalyst influencing innovation in orbital motor technology. With global industries moving toward greener solutions, future orbital motors will increasingly incorporate **improved hydraulic fluid dynamics and enhanced sealing technologies** to minimize internal losses like fluid leakage and mechanical friction. Developments in low-viscosity bio-based hydraulic fluids coupled with precise internal component engineering promise to elevate the overall efficiency of orbital motors while reducing their environmental footprint. As part of this trend, manufacturers are also focusing on reducing noise emissions by optimizing internal flow paths and improving motor casing design, catering to industries with strict noise pollution regulations.
The rise of **electrification and hybrid hydraulic systems** also impacts the future of orbital motors. While traditional orbital motors rely purely on hydraulic power, hybrid systems combining electric actuators with hydraulic motors offer enhanced control, responsiveness, and energy savings. This trend aligns with broader industry moves towards electrified machinery and smart automation, where orbital motors must adapt to seamlessly integrate with electric control systems. Innovations in power electronics and advanced control algorithms are therefore essential to optimize the interaction between hydraulic and electric components, thereby enhancing overall system performance and versatility.
Another groundbreaking area of innovation involves the use of **additive manufacturing (3D printing) techniques** for producing orbital motor components. Additive manufacturing allows the creation of highly complex internal geometries that were previously impossible or too costly to fabricate. This not only reduces production costs and lead times but also enables the design of motors with optimized internal flow channels and weight-saving structures that improve performance. Customizable motor designs facilitated by 3D printing will allow faster development cycles for niche applications and accelerate prototyping of next-generation orbital motors.
Finally, automation and robotics themselves constitute a growing market that will drive orbital motor advancements in the near future. These motors are ideally suited for mobile robots, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and other autonomous machinery due to their compact size and high torque delivery at low speeds. Future orbital motors will be designed for tighter integration with robotic control systems, offering enhanced feedback mechanisms and precise controllability that form the backbone of smarter automated equipment.
In conclusion, the ongoing innovations and emerging trends in orbital motor technology focus on smart integration, material advancements, energy efficiency, hybridization, additive manufacturing, and automation compatibility. These advancements will enable orbital motors to maintain their position as critical components across a variety of industries while transforming the way machinery operates—making them more intelligent, reliable, and environmentally friendly than ever before.
Conclusion
In conclusion, orbital motors represent a remarkable blend of efficiency, durability, and versatility, making them indispensable in a wide range of industrial applications. With 15 years of experience in the field, we have witnessed firsthand how these motors consistently deliver reliable performance under demanding conditions, empowering businesses to enhance productivity and reduce downtime. As technology continues to evolve, orbital motors remain at the forefront, offering innovative solutions tailored to meet the diverse needs of modern machinery. Whether you’re seeking enhanced torque, compact design, or superior energy efficiency, understanding and utilizing orbital motors can be a game-changer for your operations. We look forward to continuing our journey alongside our clients, driving progress with trusted expertise and cutting-edge technology.
![]() Public Mailbox: info@changjia.com
Public Mailbox: info@changjia.com
Contact us