The Role Of Hydraulic Valves In Modern Fluid Power Systems
In today’s rapidly evolving world of engineering and automation, hydraulic valves play a critical role in ensuring the precision and efficiency of fluid power systems. These unassuming yet powerful components control the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid, enabling everything from heavy machinery to advanced robotics to operate seamlessly. In this article, we’ll explore the essential functions of hydraulic valves, their impact on modern fluid power technology, and how innovations in valve design are shaping the future of industrial applications. Dive in to discover why mastering hydraulic valves is key to unlocking greater performance and reliability in fluid power systems.

- Understanding Hydraulic Valves: Fundamentals and Types
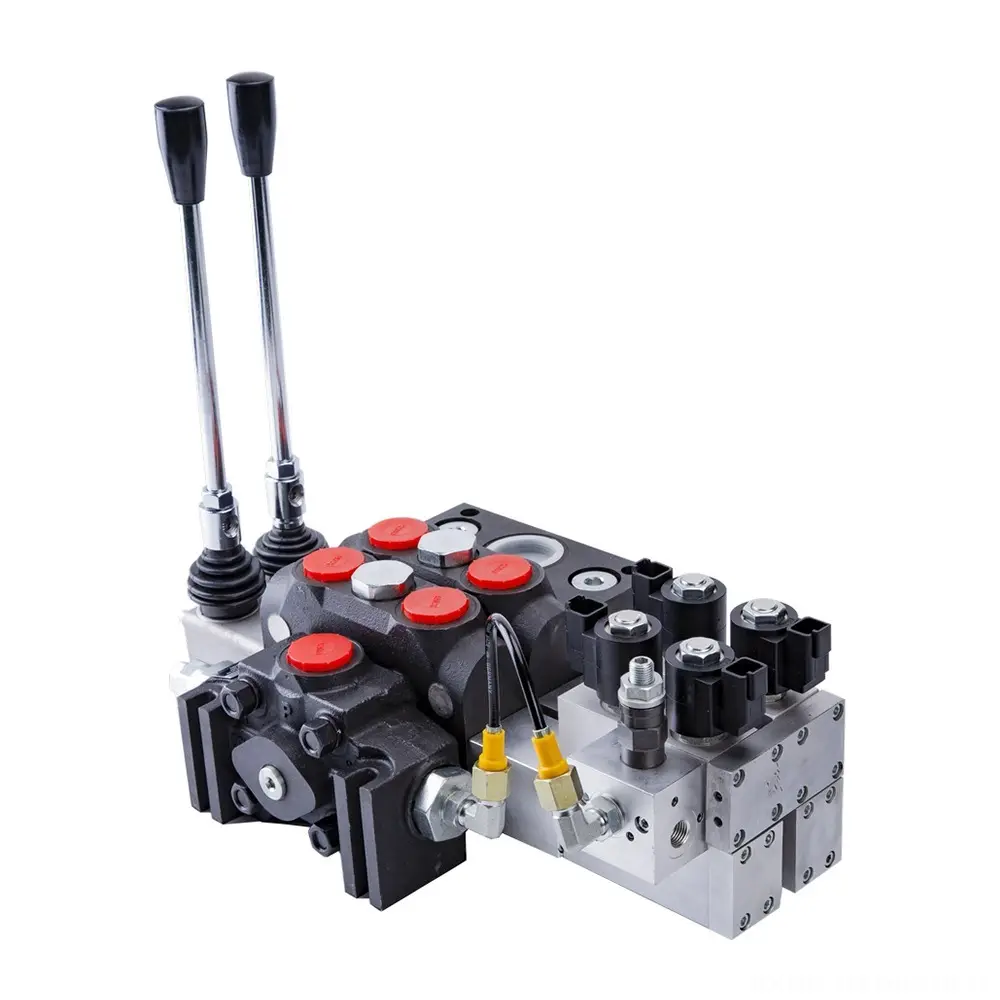
In the realm of modern fluid power systems, hydraulic valves serve as crucial components that govern the control and direction of pressurized hydraulic fluid. The hydraulic valve’s role is indispensable for ensuring the proper functioning, safety, and efficiency of hydraulic machinery across various industries, including manufacturing, construction, aerospace, and automotive sectors. Understanding the fundamentals and types of hydraulic valves is essential for engineers, technicians, and operators who work with fluid power systems.
Fundamentally, a hydraulic valve is a device designed to control fluid flow within a hydraulic circuit. It regulates the rate, pressure, and direction of the fluid, enabling machines to perform precise movements and tasks. The basic principles behind hydraulic valves involve manipulating fluid dynamics to achieve desired operational outcomes. This manipulation can mean starting or stopping fluid flow, adjusting pressure levels, or diverting fluid paths within a system.
Hydraulic valves generally consist of a housing, a spool or poppet element, and actuating mechanisms such as solenoids, levers, or pilot pressure control. The valve housing serves as the passageway for hydraulic fluid, while the spool or poppet element moves within the housing to open, close, or partially block fluid flow. Actuation mechanisms move the internal components to initiate changes in flow or pressure based on input signals or conditions.
There are several types of hydraulic valves, each designed to fulfill specific roles in fluid power systems. The primary categories include directional control valves, pressure control valves, and flow control valves.
Directional control valves are arguably the most prevalent type of hydraulic valve. They determine the path through which the hydraulic fluid travels, essentially controlling which actuators receive fluid and in what sequence. Directional valves can have multiple ports and positions, allowing complex circuit designs. For example, a 4-way, 3-position valve can route fluid to extend or retract a hydraulic cylinder or stop fluid flow altogether. These valves can be manually operated, hydraulically or pneumatically piloted, or electrically actuated via solenoids.
Pressure control valves maintain the hydraulic system’s pressures within safe and functional ranges. Overpressure conditions can damage components or reduce system reliability, so these valves are essential safeguards. Relief valves are the most common type, opening at preset pressure limits to divert excess fluid back to the reservoir or tank, preventing damage from pressure spikes. Other pressure valves include sequence valves, which activate downstream functions once a certain pressure threshold is met, and pressure reducing valves that lower pressure to auxiliary circuits to protect sensitive components.
Flow control valves regulate the volume and speed of fluid passing through the hydraulic circuit. By controlling flow rate, these valves influence the speed of hydraulic actuators, such as motors or cylinders. Fixed or adjustable orifices, needle valves, and throttle valves fall under this category. Some advanced flow control valves use compensators to maintain consistent flow despite changing pressure conditions, ensuring smooth and predictable system behavior.
Additionally, there are specialized hydraulic valves including check valves, which allow fluid flow in only one direction to prevent backflow, and unloading valves, which reduce pump load by diverting flow during idle conditions. Each type is designed to solve specific challenges encountered in hydraulic applications.
Materials and construction also play a significant role in hydraulic valve performance. Premium hydraulic valves are manufactured from high-strength metals such as steel or aluminum alloys and incorporate precision machining to achieve tight tolerances. Sealing elements and coatings resist wear and corrosion, extending valve life in harsh operating environments.
Technological advancements have further enhanced hydraulic valves’ capabilities. Modern hydraulic valves increasingly integrate electronic controls and sensors, resulting in electro-hydraulic valves that offer improved precision, programmability, and diagnostic features. These smart valves can be integrated into automated systems, providing real-time feedback and adaptive performance adjustments.
Understanding the hydraulic valve’s fundamentals and diverse types is foundational knowledge for those involved in the design, maintenance, and operation of fluid power systems. By selecting the appropriate hydraulic valve type and ensuring proper installation and control, systems can achieve maximum efficiency, reliability, and safety. The role of hydraulic valves transcends simple fluid control; they orchestrate complex machine functions and enable sophisticated applications that impact a wide range of industries worldwide.
- Key Functions of Hydraulic Valves in Fluid Power Systems
**Key Functions of Hydraulic Valves in Fluid Power Systems**
Hydraulic valves are fundamental components in fluid power systems, playing an essential role in controlling the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid to ensure proper operation and efficiency of various machinery and industrial applications. These valves, integral to the regulation and direction of fluid, enable precision and reliability in systems that rely heavily on fluid power for motion and force transmission. Understanding the key functions of hydraulic valves provides crucial insight into how modern fluid power systems achieve optimal performance.
One of the primary functions of a hydraulic valve is to **control the flow of hydraulic fluid** within the system. In fluid power circuits, controlling the flow rate is vital because it directly influences the speed of actuators such as hydraulic cylinders and motors. By regulating flow, hydraulic valves enable precise control over machine movement, ensuring operations can be adjusted dynamically according to task requirements. This control can be achieved through different types of valves like flow control valves, which modulate the fluid flow, facilitating smooth acceleration and deceleration of hydraulic actuators.
In addition to flow control, hydraulic valves play a pivotal role in **directing the flow** of hydraulic fluid along specific pathways within the circuit. Directional control valves are specialized hydraulic valves designed to guide the fluid to particular parts of the system, allowing machinery to perform different functions with versatility. For example, a directional control valve can switch the flow between extending or retracting a hydraulic cylinder, enabling the device to execute complex motions. This directional control is central to automating fluid power machinery, where different operations may be needed in sequential or simultaneous patterns.
Another essential function of hydraulic valves is to **regulate pressure within the system**. Hydraulic systems generally operate under high pressure to generate the necessary force for heavy-duty applications. Pressure control valves help maintain system safety and efficiency by preventing excessive pressure buildup that could damage components or cause system failure. These valves can include relief valves, pressure reducing valves, and sequence valves, each designed to maintain pressure within defined limits or to sequence the activation of different system parts based on pressure thresholds.
Hydraulic valves also contribute to **system stability and efficiency** by minimizing losses and preventing backflow. Non-return valves, also known as check valves, are a key example. They allow fluid to flow only in one direction, preventing reverse flow that could lead to inefficiencies or damage. By maintaining unidirectional flow, these valves help sustain the operational integrity and responsiveness of fluid power systems.
The **modulation of hydraulic energy** via valves is critical, especially in systems requiring fine adjustments. Proportional and servo valves exemplify this function by offering variable control over flow and pressure rather than the simple open-or-close operation typical of conventional on/off valves. This modulation capability allows for more nuanced control over actuators, improving the precision and smoothness of operations, which is highly beneficial in applications such as robotics, aerospace, and manufacturing automation.
Beyond control functions, hydraulic valves enable **system automation and safety** features. Automated hydraulic valves, integrated with electronic controls, allow fluid power systems to operate with minimal manual intervention, adapting quickly to changing conditions through feedback loops and sensors. Safety valves act as fail-safe devices, engaging when irregular system conditions or emergencies arise to protect both the equipment and operators.
Moreover, hydraulic valves contribute to the **energy efficiency** of fluid power systems. By effectively managing fluid flow and pressure, these valves reduce unnecessary energy consumption and heat generation caused by turbulence and pressure drops. Improved energy efficiency means lower operational costs and longer system life.
In modern fluid power systems, hydraulic valves are designed with advanced materials and precision engineering to withstand harsh environments, high pressures, and rapid cycling. They are indispensable components that ensure the **reliable, flexible, and safe operation** of complex machinery across industries such as construction, manufacturing, agriculture, and transportation.
In summary, the key functions of hydraulic valves—flow control, directional control, pressure regulation, prevention of backflow, modulation of hydraulic power, system automation, safety, and efficiency—define their critical role in fluid power systems. Mastery of these functions is essential for engineers and technicians aiming to leverage hydraulic technology to its fullest potential in modern industrial applications.
- Impact of Hydraulic Valves on System Efficiency and Performance
**Impact of Hydraulic Valves on System Efficiency and Performance**
Hydraulic valves are fundamental components in modern fluid power systems, playing a pivotal role in regulating the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid to ensure optimal system operation. Their impact on system efficiency and performance cannot be overstated, as they directly influence the responsiveness, precision, energy consumption, and overall reliability of hydraulic machinery. Understanding how hydraulic valves contribute to these factors provides valuable insight into why they are indispensable in fluid power applications across industries such as manufacturing, construction, aerospace, and automotive sectors.
At the core, hydraulic valves control the direction, pressure, and flow rate of hydraulic fluid within a circuit. By precisely managing these parameters, hydraulic valves ensure that actuators—such as hydraulic cylinders and motors—receive the right amount of fluid at the right time and pressure. This precise control translates into enhanced system performance, allowing machinery to execute complex, smooth, and accurate motions. Without effective valve control, hydraulic systems would suffer from inefficiencies including sluggish response times, unintended movements, or even complete system failure.
One of the key impacts of hydraulic valves on system efficiency is their influence on energy consumption. Hydraulic systems inherently involve energy loss due to fluid friction, leakage, and pressure drops across components. High-quality valves with well-designed spools and seals minimize these losses by reducing internal leakage and optimizing flow paths. For example, proportional and servo valves enable variable control of fluid flow and pressure, which means the system can be tuned dynamically according to the load requirements rather than operating at full capacity all the time. This adaptability significantly reduces wasted energy, contributing to improved fuel efficiency in mobile equipment and lower operating costs in industrial setups.
Furthermore, hydraulic valves enhance safety and reliability, underpinning performance by preventing dangerous pressure spikes and uncontrolled fluid flow. Pressure relief valves protect downstream components from damage by releasing excess pressure, while check valves prevent reverse flow that could otherwise disrupt machine operation or cause hazards. In scenarios involving high-speed or heavy load applications, precise valve operation ensures that the system maintains stability under varying operating conditions. This stability is essential not only for machine performance but also for operator safety and the longevity of equipment.
Another impact on performance is observed in the accuracy and repeatability of hydraulic systems. Modern hydraulic valves, such as proportional valves and servo valves, are capable of fine modulation of flow rates and pressures with high resolution and responsiveness. This capability allows for tight control loops in automated systems, producing consistent and repeatable outputs critical in applications like CNC machines and robotics. The inherent deadband, hysteresis, and response time of valves influence how quickly and precisely these adjustments can be made, thus directly affecting the quality and efficiency of the manufacturing processes they support.
Maintenance and operational uptime are also affected by the design and quality of hydraulic valves. Valves with robust construction and reliable sealing can withstand harsh operating environments with minimal wear, reducing downtime caused by leaks, jamming, or component failure. This reduction in maintenance intervals directly boosts system availability and productivity. Moreover, advanced valve technologies incorporating electronics and smart controls offer diagnostic capabilities that can preemptively warn operators of performance degradation, thereby enabling proactive maintenance strategies.
In sum, hydraulic valves are critical determinants of the efficiency and performance characteristics of fluid power systems. Their design and operational features impact energy usage, control precision, safety, reliability, and maintenance. As hydraulic technology continues to evolve, innovations in valve materials, designs, and control methods will further enhance fluid power systems’ effectiveness, ensuring that hydraulic valves remain at the heart of modern hydraulic machinery.
- Advances in Hydraulic Valve Technology for Modern Applications
**Advances in Hydraulic Valve Technology for Modern Applications**
Hydraulic valves serve as the fundamental control elements in fluid power systems, directing the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid to perform a wide array of mechanical functions. Over the decades, advancements in hydraulic valve technology have been pivotal in enhancing the efficiency, precision, and reliability of modern fluid power systems. As industries demand higher performance and smarter solutions, the evolution of hydraulic valves has matched these needs, integrating innovative materials, design enhancements, and intelligent control systems that altogether push the boundaries of what can be achieved in hydraulic applications.
One of the most significant advances in hydraulic valve technology is the development of proportional and servo valves. Unlike traditional directional and relief valves that operate in discrete positions (fully open or fully closed), proportional and servo valves allow for precise modulation of flow and pressure. This fine control capability is essential in applications that require smooth and variable motion such as robotics, aerospace, and advanced manufacturing systems. These valves respond to electronic signals, translating them into mechanical movement with high responsiveness, enabling complex motion profiles and energy-efficient operation.
Modern hydraulic valves also benefit immensely from improvements in materials and manufacturing techniques. Enhanced materials such as advanced alloys and composites offer increased wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and longer service life under harsh operating conditions. This is particularly critical in mobile hydraulic systems and industrial machinery operating in extreme environments—such as mining, marine, and construction. Additionally, precision machining technologies, including CNC manufacturing and additive manufacturing (3D printing), allow for more intricate valve designs with tighter tolerances. This results in improved sealing, reduced internal leakage, and better overall valve performance, directly contributing to system efficiency and reliability.
Integration of electronics and smart technology represents another breakthrough in hydraulic valve technology. Modern hydraulic valves are increasingly equipped with sensors, embedded processors, and connectivity features that enable real-time monitoring and control. These smart valves can measure parameters such as pressure, temperature, and flow rate, providing valuable data for predictive maintenance and system diagnostics. By enabling closed-loop control systems, smart hydraulic valves optimize system performance automatically, adjusting flow and pressure dynamically in response to changing operational demands. Such intelligent control not only enhances precision but also reduces energy consumption and downtime, facilitating more sustainable and cost-effective fluid power solutions.
The rise of digital hydraulics is closely linked to these innovations. Digital hydraulic valves use pulse-width modulation and on/off solenoid valves to achieve precise flow control digitally rather than through analog means. This technique simplifies valve design and allows for rapid switching, which provides high-speed control of hydraulic actuators. Digital hydraulics is emerging as a promising platform in applications requiring ultra-fast response and high power density, such as in advanced manufacturing automation and mobile machinery.
Another important trend in hydraulic valve technology is miniaturization. As machinery and systems, particularly in robotics and aerospace, become more compact, the demand for smaller hydraulic components with equal or enhanced capability intensifies. Miniature hydraulic valves now offer reduced size and weight without compromising performance. These valves enable fluid power to be applied in domains previously unimaginable for hydraulic systems, thus broadening the scope of applications where hydraulic valves can be deployed effectively.
Furthermore, environmental considerations are influencing hydraulic valve design and technology. The industry is moving towards valves compatible with biodegradable and environmentally friendly hydraulic fluids. Advances in sealing technologies and materials ensure these valves maintain optimal performance while minimizing fluid leakage and environmental contamination. This development aligns with global efforts to promote greener industrial practices without sacrificing the robustness and reliability of fluid power systems.
In summary, advances in hydraulic valve technology are a key driver behind the enhanced capabilities of modern fluid power systems. Through innovations in proportional control, material science, smart technology integration, digital hydraulics, miniaturization, and environmental compatibility, hydraulic valves continue to evolve and adapt to the complex demands of today’s industrial and mobile applications. These advancements empower engineers and operators with more efficient, precise, and reliable solutions that sustain the vital role of hydraulic valves in modern fluid power systems.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Hydraulic Valves in Fluid Power Systems
**Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Hydraulic Valves in Fluid Power Systems**
Hydraulic valves are critical components in modern fluid power systems, serving as the control elements that regulate the direction, pressure, and flow rate of hydraulic fluid within the system. Proper maintenance and effective troubleshooting of hydraulic valves are essential to ensure the reliability, efficiency, and longevity of the entire hydraulic system. This article delves into the essential practices for maintaining hydraulic valves and outlines common troubleshooting techniques to address operational issues.
### Importance of Maintenance for Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic valves operate under high pressures and often in harsh environments, making regular maintenance a prerequisite for preventing premature failure. Over time, contaminants such as dirt, water, and metal particles can accumulate within the valve components, leading to wear, corrosion, or blockages. Additionally, seals and internal springs may degrade, causing leaks or improper valve response.
Preventive maintenance for hydraulic valves typically involves several tasks:
1. **Inspection and Cleaning:** Routine inspection helps detect external damage or leaks early. Cleaning the valve surfaces and the hydraulic fluid helps minimize contamination risks.
2. **Fluid Monitoring and Replacement:** Hydraulic fluid quality directly affects valve performance. Oil analysis can identify contamination, moisture content, and degradation. Regular fluid replacement and filtration preserve valve integrity.
3. **Seal and Component Replacement:** Seals are prone to wear due to continuous pressure cycles, temperature variations, and fluid exposure. Replacing seals, O-rings, and springs during maintenance stops potential leakage and sticking problems.
4. **Lubrication:** Certain valve types require lubrication to reduce friction among moving parts. Appropriate lubricants must be used to prevent deterioration of seals or compatibility issues with hydraulic fluids.
5. **Calibration and Testing:** Some hydraulic valves, especially proportional and servo valves, need periodic calibration to maintain precise control. Functional testing ensures that valves respond correctly to control inputs.
### Common Symptoms Indicating Hydraulic Valve Problems
Recognizing problems early is key to minimizing downtime and costly repairs. Symptoms of faulty hydraulic valves may include:
- Erratic movement or jerky performance of hydraulic actuators.
- Unexpected pressure fluctuations or the inability to achieve required system pressures.
- Loud noises such as knocking or hammering within the hydraulic lines.
- External oil leaks around valve bodies or connections.
- Excessive heat generation within the hydraulic system.
- Failure of the valve to shift positions properly or slow response times.
### Troubleshooting Techniques for Hydraulic Valves
Troubleshooting hydraulic valves requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the malfunction:
1. **Visual and Physical Inspection:** Begin by examining the valve for external damage, loose fittings, and leaks. Check for contamination in hydraulic fluid and evaluate the condition of seals and hoses.
2. **Check System Pressure and Flow:** Using pressure gauges and flow meters can help isolate valve-related issues from other system components. Low pressure or insufficient flow may indicate valve blockage, spool sticking, or incorrect valve settings.
3. **Valve Disassembly and Cleaning:** If contamination or sticking is suspected, carefully disassemble the valve and clean all internal parts with appropriate solvents. Inspect internal surfaces for wear, scoring, or corrosion.
4. **Seal and O-Ring Replacement:** Worn or damaged seals can lead to internal leakage and valve malfunction. Replacing seals typically restores proper operation.
5. **Functional Testing:** After maintenance, perform bench testing of individual valves to verify proper spool movement and response before reinstalling in the system.
6. **Electrical and Control Signal Verification:** For electrically actuated or proportional valves, checking solenoid coils and electrical connections is essential. Use diagnostic tools to verify the control signals and valve positioning feedback.
### Advanced Diagnostic Tools and Technologies
Modern fluid power systems often incorporate diagnostic features to simplify maintenance of hydraulic valves. Technologies such as pressure sensors, flow sensors, and electro-hydraulic position feedback enable real-time monitoring of valve performance. Condition-based maintenance systems analyze sensor data to predict upcoming failures and schedule timely interventions.
Furthermore, portable diagnostic devices can perform on-site testing of valve characteristics, including leakage rates, response times, and control signals. This reduces system downtime and allows maintenance personnel to perform precise troubleshooting without extensive system disassembly.
### Best Practices for Maintaining Hydraulic Valve Performance
To maximize the lifespan and reliability of hydraulic valves:
- Use high-quality hydraulic fluids and maintain fluid cleanliness standards.
- Establish routine inspection and maintenance schedules tailored to operational conditions.
- Train maintenance personnel in proper valve handling, disassembly, and reassembly procedures.
- Store spare parts, especially seals and critical components, to facilitate quick repairs.
- Leverage monitoring and diagnostic tools for proactive condition assessment.
Through diligent maintenance and systematic troubleshooting, hydraulic valves will continue to serve as the vital control elements in modern fluid power systems, ensuring efficiency and performance in demanding industrial applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydraulic valves remain the cornerstone of modern fluid power systems, ensuring precise control, efficiency, and reliability across a multitude of applications. With 15 years of industry experience, our company has witnessed firsthand how advancements in valve technology continue to drive innovation and performance improvements in hydraulic machinery. As fluid power systems evolve to meet the demands of tomorrow’s industries, the importance of high-quality, expertly engineered hydraulic valves will only grow. We are proud to be at the forefront of this journey, delivering solutions that empower our clients to achieve greater productivity and operational excellence.
![]() Public Mailbox: info@changjia.com
Public Mailbox: info@changjia.com
Contact us